Battery Thermal Management_Cell Foam Materials
Foam is a material that has been foamed by plastic particles, referred to as foam. Foam has a series of characteristics such as elasticity, light weight, fast pressure-sensitive fixation, convenient use, free bending, ultra-thin volume, and reliable performance. Foam is divided into PU foam, anti-static foam, conductive foam, EPE, anti-static EPE, CR, EVA, bridging PE, SBR, EPDM, etc.
The power battery system is generally mainly composed of battery modules, battery management systems BMS, thermal management systems, and some electrical and mechanical systems. At present, the factors affecting the large-scale promotion and application of new energy vehicles include battery system cost, cruising range, and battery system safety. With the development of new energy vehicle technology, more and more attention has been paid to safety. In the case of overcharging, acupuncture, and collision, power lithium-ion batteries can easily cause a chain exothermic reaction and cause thermal runaway, resulting in smoke, fire or even explosion. At the same time, the performance of power batteries, including energy density and service life, is affected by temperature changes, so the importance of thermal management is further reflected.

The importance of thermal management
Under different driving conditions of the vehicle, due to its own internal resistance, the single cell will generate a certain amount of heat while outputting electric energy, making its own temperature higher. When its own temperature exceeds its normal working temperature range, it will Affect battery performance and life. The power battery system on an electric vehicle is composed of multiple power battery cells. The power battery system generates a large amount of heat during operation and accumulates in the small battery box. If the heat cannot be quickly dissipated in time, the high temperature It will affect the life of the power battery and even cause thermal runaway, resulting in fire and explosion.
At present, domestic thermal management research focuses more on heat dissipation, more precisely on the battery system box and module level, such as the application of liquid cooling systems. The thermal insulation prevention and control at the cell level has not paid much attention. It can be seen from the design of the power battery system that the two-level structure of the battery cell and the battery module needs to be considered when designing the thermal management system. Therefore, in the overall design of the battery system, the influence of the temperature environment of the location of the battery cell and the battery module must be considered. Therefore, when designing the arrangement of battery modules, if the single cells are compactly arranged and there is no heat dissipation and heat insulation measures, the temperature of the battery pack will rise sharply during charging and discharging, and there is a serious safety hazard.
Therefore, it is necessary to strengthen the heating and heat dissipation capacity of the battery through the research of battery thermal management technology to ensure that the battery works within a suitable temperature range and maintain a reasonable temperature distribution in the battery box. Research needs to be gradually extended from the generation mechanism and characteristics of thermal runaway at the single level to the level of thermal runaway triggered by single thermal runaway and then propagated to the entire battery system.
Second, the difference between whether there are thermal insulation measures
Studies have shown that an insulating layer is installed between the battery cells to block the heat transfer from the runaway cells to the adjacent cells. The heat generated by the body is dissipated in the entire battery pack to avoid local overheating. In "Research on Thermal Protection and Heat Dissipation Integration of Vehicle Power Batteries", four schemes are set up to analyze the thermal performance during thermal runaway. Scheme 1 means that no heat dissipation measures are added between battery cells, and scheme 2 represents between battery cells. Place heat shields. Option 3 represents the placement of heat pipe groups between battery cells. Option 4 represents staggered placement of heat shields and heat pipe sets between cells.
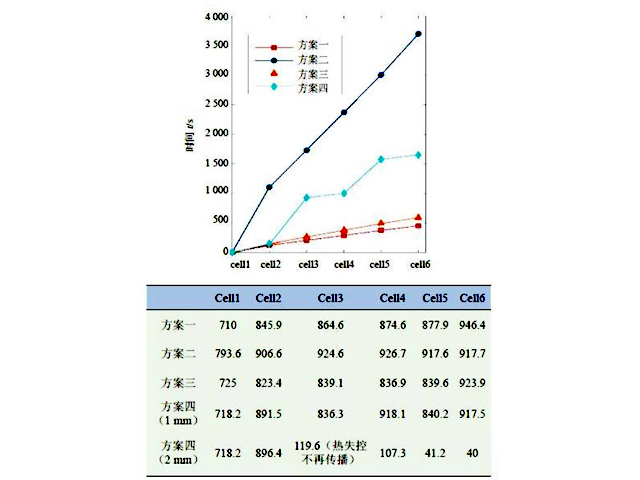
The heat dissipation and thermal insulation performance of the battery pack under normal operating conditions and thermal runaway under the four schemes are analyzed, the thermal management performance of the integrated system is compared and verified, and the barrier effect of the thickness of the thermal insulation board on the propagation of thermal runaway is explored. The conclusions are as follows:
(1) The comparison of the four schemes shows that the second scheme has outstanding thermal resistance and can effectively delay the spread of thermal runaway, but the heat dissipation performance is poor, and only relying on the heat shield and natural heat dissipation cannot meet the thermal management requirements of the battery pack. Scheme 3 has good heat dissipation performance, but the maximum temperature difference rises sharply with the increase of the discharge rate. At the same time, the thermal resistance performance after the thermal runaway is triggered is much lower than that of scheme two and scheme four. Solution 4 not only greatly enhances the heat dissipation capability of the battery pack and the temperature uniformity of each cell in the battery pack, but its high thermal insulation performance can also effectively block the spread of thermal runaway.
(2) By changing the thickness of the heat shield, the heat dissipation capability of the battery pack can be enhanced, which can effectively block the spread of thermal runaway. When the thickness of the heat insulation board is increased from 1mm to 2mm, the thermal runaway can be blocked before the heat insulation board under the premise of ensuring the normal operation of the heat pipe.
(3) The combination of reasonable thermal insulation measures and cooling methods can not only effectively improve the stability of the operating temperature range of the battery pack, but also effectively block thermal runaway.
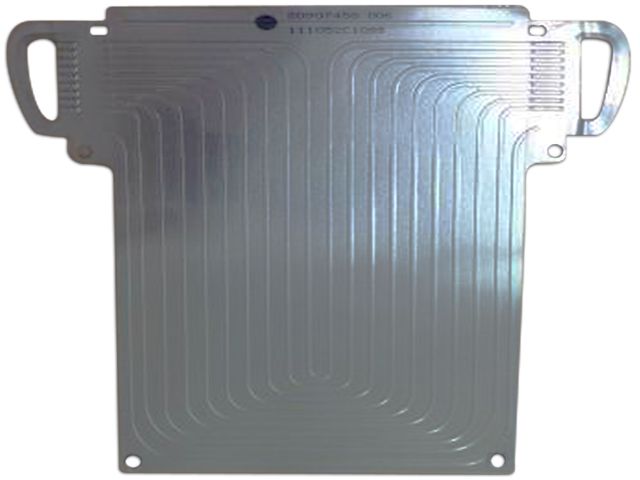
The more classic is the battery thermal management system of General Motors Volt, which uses liquid-cooled heat dissipation. A metal heat sink (1mm thick) is arranged between the single cells, and a capillary structure is left on the heat sink, so that the cooling liquid can flow in the capillary to take away heat and achieve the purpose of heat dissipation. The thermal insulation scheme adopts the method of placing foam between the cells and the cells.
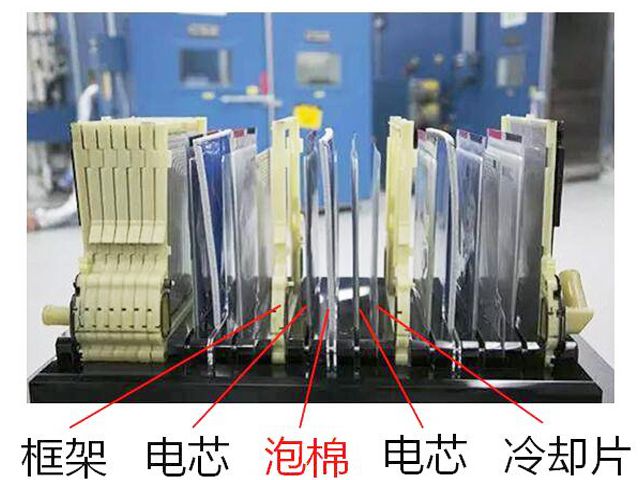

Third, the application of foam
The battery system and module are generally designed according to the structure and shape of the battery cells. The battery cells are mainly divided into three types: cylindrical cells, square cells and soft packs. Due to the higher energy density of soft-packed cells than the other two, the application of soft-packed cells will also increase relatively under the influence of the energy subsidy policy. The advantage of the soft package is that the external structure has little influence on the cell, the cell has excellent performance, and the quality of the material used in the package is small. However, the disadvantages are also obvious. The sealing process of large-capacity batteries is more difficult and the reliability is relatively poor. In addition, the aluminum-plastic composite packaging film used has low mechanical strength, and the service life of the aluminum-plastic composite film restricts the service life of the battery.
Therefore, it is necessary to consider the bulging of the soft pack during charging and discharging. If the soft pack and the soft pack are directly rubbed for a long time, the aluminum-plastic film may be damaged, causing the battery to fail or even out of control. Therefore, the application of foam in the middle of soft-packed cells is very important, which is manifested in the following four aspects:
1. The foam has low hardness and high resilience, which can absorb the bulging stress of the battery and play a buffering role;
2. When the cell transmits heat out of control, the foam can act as heat insulation, inhibit heat diffusion, and delay the occurrence of accidents;
3. When the cell is on fire, the flame retardant effect of foam can delay the spread of the fire and increase the escape time;
4. Foam has excellent resilience and wide compression ratio, which can be used as positioning.
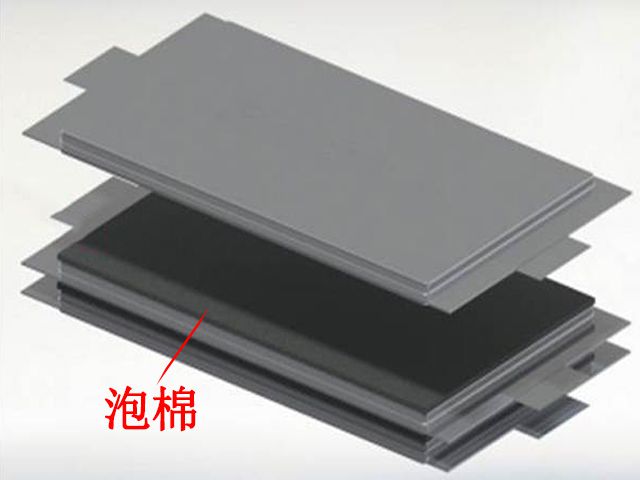
There are many types of foam, including PU, PE, CR and EVA. In the actual application process of the battery system, it is found that only foams that can maintain sufficient elastic recovery ability in a long-term compression environment, such as PU, are suitable for use between soft-packed cells, and others, such as CR, recover after long-term compression. The deterioration of the ability causes the module structure to fall apart. Therefore, it is necessary to consider the elastic modulus and rebound rate of the foam when designing and applying foam in the module.
In addition, through the disassembly and analysis of the VOLT module structure, the applied foam does not appear to be self-extinguishing from the fire, which means that it is not the V0 required by the national standard, which is also an interesting point. Perhaps its thermal insulation ability is quite good and the effect of the liquid cooling system can avoid the occurrence of thermal runaway. Or if there is thermal runaway, it has already burned anyway, and flame retardant will not play a big role.



